The results of the Global Risks Report 2024 indicated a risk landscape where economic, geopolitical, and societal vulnerabilities will continue to rise. This is evident in 2025 with the intensification of climate-related disasters, escalating geopolitical tensions, and the ongoing impacts of inflation on global markets.
These trends underscore the urgent need for organizations to adopt robust risk mitigation strategies to safeguard their operations and ensure resilience.
The gap between exposure and preparation leaves organizations vulnerable to financial losses, regulatory penalties, and irreparable damage to their reputation. Risk mitigation is essential for modern business resilience.
For organizations operating in regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing, effective risk mitigation strategies aren’t just recommended; they’re essential for survival.
This guide examines the fundamental principles of risk mitigation, explores proven strategies, and provides actionable best practices that organizations can implement immediately.
What is risk mitigation?
Risk mitigation is the process of identifying potential threats to an organization and implementing strategic measures to eradicate them or minimize their impact. Unlike reactive crisis management, risk mitigation focuses on prevention and preparation, creating robust defenses before threats emerge.
Risk intelligence monitoring uses advanced technology, machine learning, and a vast network of vetted data sources to provide real-time, hyper-local insights into potential threats. Platforms such as the Everbridge Risk Intelligence Monitoring Center (RIMC) ensure organizations receive targeted alerts, enabling swift and informed decision-making to protect people, assets, and supply chains.
The purpose of risk mitigation extends beyond simple problem-solving. It encompasses protecting business continuity, preserving stakeholder trust, maintaining regulatory compliance, and safeguarding financial stability.
Risk mitigation operates as a critical component within the broader risk management framework, which includes risk identification, assessment, treatment, and monitoring. While risk management provides the strategic oversight, risk mitigation delivers the tactical execution that transforms vulnerability into resilience.
Types of risks organizations face
Organizations face multiple types of risk, each requiring tailored approaches and specialized expertise.
Compliance risks
This emerges when organizations fail to adhere to legal, regulatory, or industry standards. A missed compliance deadline can cost finance firms millions in fines, while healthcare organizations face potential patient safety violations that carry both financial and legal consequences.
Operational risks
The results from inadequate or failed internal processes, systems, or human factors. Manufacturing facilities face equipment failures, supply chain disruptions, and quality control issues that can halt production and damage customer relationships.
Reputational risks
This threatens the trust and confidence that stakeholders place in an organization. A single data breach or product recall can erode years of brand building, particularly in sectors where public trust is paramount.
Cybersecurity risks
One of the most pressing and common concerns for organizations. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and system infiltrations can compromise sensitive information, disrupt operations, and expose organizations to significant financial and legal liabilities.
Financial risks
This encompasses market volatility, credit defaults, liquidity constraints, and currency fluctuations that can impact an organization’s financial stability and growth trajectory.
Join us on November 19, 2025, for our webinar, The 2026 Global Risk and Resilience Outlook. Discover valuable insights into emerging risk trends and effective resilience strategies to prepare for the year ahead.
What is a risk mitigation strategy?
A risk mitigation strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines specific actions and procedures designed to reduce an organization’s exposure to identified risks. These strategies serve as the blueprint for building organizational resilience, ensuring business continuity, and protecting stakeholder interests.
Effective risk mitigation strategies focus on these core objectives: identifying potential threats and assessing them, prioritizing risks based on their potential impact and likelihood, and implementing targeted interventions that address each risk category. This systematic approach enables organizations to allocate resources efficiently while maintaining operational effectiveness.
The most effective risk mitigation strategies are tailored to an organization’s unique operational environment, industry requirements, and risk tolerance.
5 Risk mitigation strategies
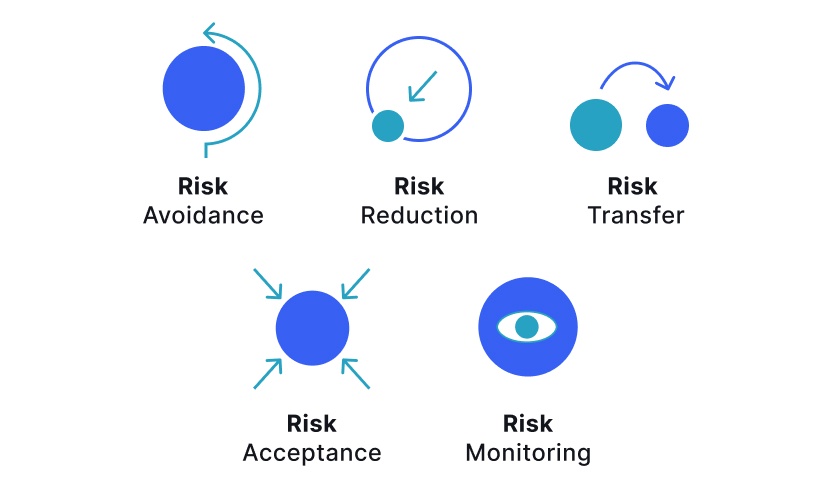
Organizations across industries adopt various risk mitigation strategies tailored to their specific needs. Here are the most common approaches with examples:
1. Risk avoidance
Risk avoidance involves eliminating activities or processes that pose significant threats to organizational objectives. This strategy proves particularly effective when the potential impact far outweighs any possible benefits.
For example:
- Financial institutions may relocate operations from politically unstable regions to protect assets and personnel.
- Tech companies might avoid entering markets with restrictive data privacy laws to reduce regulatory risks.
2. Risk reduction
Risk reduction strategies focus on implementing measures that decrease either the likelihood of a risk occurring or minimize its potential impact. This approach allows organizations to continue beneficial activities while reducing associated threats.
For example:
- Manufacturing plants use fire suppression systems, safety talks and training, and emergency shutdown protocols to prevent workplace accidents.
- Healthcare organizations implement redundant data backups and strict access controls to mitigate cybersecurity risks.
3. Risk transfer
Risk transfer involves shifting the burden of potential losses to third parties, typically through insurance policies or contractual agreements. This strategy provides financial protection while allowing organizations to maintain their operations.
For example:
- Businesses purchase cybersecurity insurance to cover legal fees, notification costs, and penalties from data breaches.
- Construction companies transfer risks to contractors with liability coverage in their agreements.
4. Risk acceptance
Risk acceptance acknowledges that certain threats are inherent to operations and that the cost of mitigation may exceed the potential benefits. Organizations using this strategy maintain awareness of accepted risks while implementing monitoring systems to detect changes in threat levels.
For example:
- Startups often accept market risks tied to new product launches, embracing uncertainty as part of innovation.
- Established companies may tolerate minor operational risks with minimal business impact.
5. Risk monitoring
Risk monitoring involves continuous surveillance of the threat landscape, enabling organizations to detect emerging risks and adapt their mitigation strategies accordingly. This dynamic approach ensures that risk management remains effective as conditions change.
For example:
- Financial institutions use AI tools to detect fraudulent activities quickly.
- Supply chain managers leverage predictive analytics to anticipate and prevent disruptions.
6 Steps to create a successful risk mitigation strategy
1. Identify risks
Begin by thoroughly identifying potential risks that could impact the organization. Analyze all aspects of the business, such as operations, financial practices, cybersecurity, and supply chains. Utilize tools like SWOT analysis, risk assessments, and historical data reviews to ensure comprehensive risk identification.
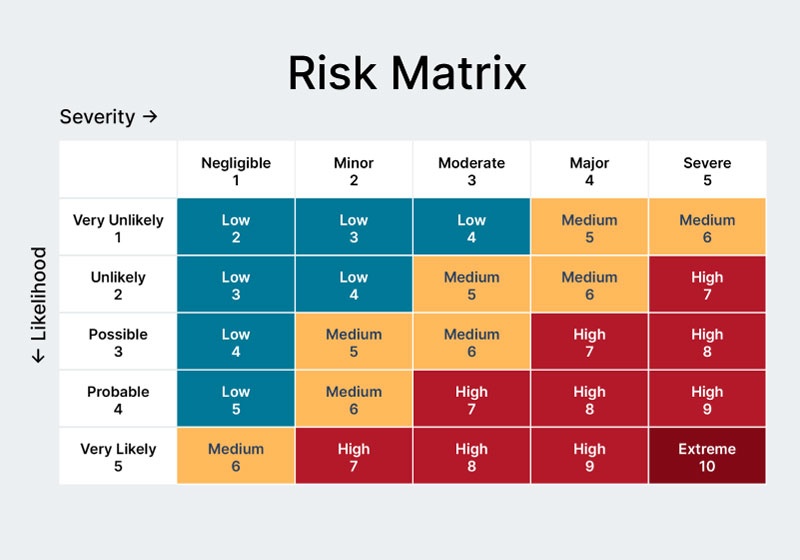
2. Assess risk impact and likelihood
Once risks are identified, evaluate their potential impact and the likelihood of occurrence. This assessment enables prioritization, allowing resources to focus on mitigating risks that pose the most significant threat to business continuity and objectives.
3. Develop mitigation plans
Design actionable plans to minimize the impact of high-priority risks. This may involve implementing preventative measures, establishing backup systems, or defining response protocols. Engage with stakeholders across departments to ensure a collaborative and robust strategy.
4. Implement risk controls
Deploy the mitigation measures outlined in the plan. This involves integrating controls into daily operations, such as training employees on risk management procedures, upgrading systems to strengthen cybersecurity defenses, utilizing risk intelligence tools, or diversifying suppliers to reduce dependency.
5. Monitor and review
Continuous monitoring of the implemented strategy is crucial to its success. Establish performance indicators to measure the effectiveness of risk mitigation efforts and review them regularly. Adapt your strategy as new risks emerge or business contexts evolve, ensuring it remains relevant and efficient.
6. Foster a risk-aware culture
Cultivate an organizational culture where proactive risk identification and response are prioritized. Encourage open communication and empower employees to report potential risks. A risk-aware culture ensures the entire organization is aligned and resilient in the face of challenges.
Addressing the “Expanding Risk Zone” with the Everbridge High-Velocity CEM Platform
The “Expanding Risk Zone” represents a new reality for organizations worldwide. The rising frequency and intensity of critical events—such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, geopolitical conflicts, and public health crises—are fundamentally reshaping the priorities of executive teams and boardrooms alike. These challenges are placing unprecedented pressure on operational continuity and organizational resilience. Seamless operations now hinge on the ability to anticipate, respond to, and recover from an increasingly complex and evolving risk landscape.
The Everbridge High Velocity CEM platform is uniquely designed to support organizations as they tackle the demands of this expanding risk zone. Powered by Purpose-built AI, High Velocity CEM helps leaders understand risks earlier and respond faster. By integrating advanced analytics, real-time monitoring, and automated workflows, Everbridge enables organizations to proactively assess threats, minimize downtime, and maintain operational efficiency.
Building resilience with strategic risk management
The modern business environment demands proactive risk management approaches that anticipate threats and implement effective countermeasures. Organizations that invest in comprehensive risk mitigation strategies and technologies protect themselves from potential disruptions while positioning themselves for sustainable growth.
Success in risk mitigation requires commitment from all organizational levels, supported by robust technology platforms and continuous improvement processes. Organizations that embrace this comprehensive approach to risk management create competitive advantages that extend far beyond simple threat protection.
Protect your organization from unexpected disruptions and build the resilience necessary for long-term success.
Join our webinar on November 19, 2025, The 2026 Global Risk and Resilience Outlook, for insights on emerging risks and strategies to prepare for the future.